Prostista
Kingdom
What
is a Protist?
Protists
are organisms that are classified into the kingdom Protista. The protists
form a group of organisms that really do not fit into any other kingdom.
Although there is a lot of variety within the protists, they do share some
common characteristics.
All
protists are eukaryotic.
That is, all protists have cells with nuclei. In addition, all protists live
in moist environments.
Protists
can be unicellular
or multicellular.
Protists can be microscopic or can be over 100 meters (300 feet) long. Some
protists are heterotrophs,
while others are autotrophs.
Since
protists vary so much, we will group them into three subcategories: animal-like
protists, fungus-like
protists, and plant-like
protists.
Protists
that are classified as animal-like are called protozoans
and share some common traits with animals. All animal-like protists are heterotrophs.
Likewise, all animal-like protists are able to move in their environment in
order to find their food. Unlike, animals, however, animal-like protists are
all unicellular.
Animal-like
protists are divided into four basic groups based on how they move and live.
|
Phylum
|
Characteristics
|
Example
|
Description
|
Mastigophorans
|
Protists
with flagella
|
The
Giardia is another example of this type of animal-like
protist.
|
These
protists move by beating their long whiplike structures called flagella.
These protists can have one or more flagella that help them
move. Many of these protists live in the bodies of other
organisms. Sometimes, they help their host, while at other times
they harm their host.
|
|
Sarcodines
|
Protists
with pseudopods
|
Amoeba
|
These
protists move by extending their bodies forward and then pulling
the rest of their bodies forward as well. The finger-like
structures that they project forward are called pseudopods.
The pseudopods are also used to trap
food.
|
|
Sporozoa
|
Parasitic
protists
|
Plasmodium
|
|
|
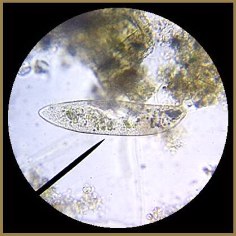
Ciliates
|
Protists
with cilia
|
Paramecium
|
These
protists move by beating tiny hair-like structures called cilia.
The cilia act as tiny oars that allows the protist to move
through its watery environment. The cilia also help the protists
capture food.
|
Protozoans
- "Animal-like" protista


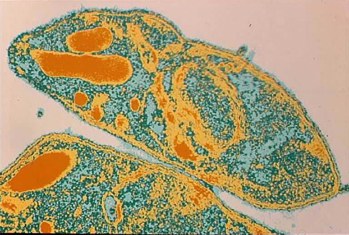
Fungus-like
protists are heterotrophs
with cell walls. They also reproduce by forming spores.
All fungus-like protists are able to move at some point in their lives.
There are essentially three types of fungus-like protists: water molds,
downy mildews, and slime molds.
|
Phylum
|
Characteristics
|
Example
|
Description
|
Myxomycota
Acrasiomycota
|
Heterotrophic,
amoeboid mass called plasmodium
Heterptrophic,
separate cells
|
other
|
|
 |
Heterotrophs
with cell walls,
reproduce
by forming spores,
able
to move at some point in their lives
|
|
|
 |
Heterotrophs
with cell walls,
reproduce
by forming spores,
able
to move at some point in their lives
|
|
Fungus
Like Protists

Plasmodial
Slime Mold

Cellular
slime molds

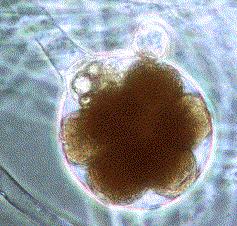

Plant-like
protists are autotrophic.
They can live in soil, on the bark of trees, in fresh water, and in salt
water. These protists are very important to the Earth because they produce a
lot of oxygen, and most living things need oxygen to survive. Furthermore,
these plant-like protists form the base of aquatic food chains.
These
plant-like protists can be unicellular,
multicellular,
or live in colonies.
The plant-like protists are divided into three basic groups: euglenoids,
diatoms
/ algae and dinoflagellates
|
Phylum
|
Characteristics
|
Example
|
Description
|
Euglenophytes
|
Unicellular,
photosynthetic, single flagellum
|
|
|
Chrysophytes
|
Unicellular,
photosynthetic, chlorophyll a and c
|
|
|
 |

|
Green
Algae
|
|
 |

|
Red
Algae
|
|
 |

|
Brown
Algae
|
|
Dinoflagellates
|
Unicellular,
two spinning flagella, chlorophyll a and c
|
Gessnerium
|
|




Sporozoans



VOCABULARY:
person; the
disease is characterized by high fevers that alternate with severe chills
Flagellates
- move like the Euglena
Mastigophora
Often have
more than one flagellum
The
organism which causes African sleeping sickness - carried by the testie fly
Some live
in the digestive tracts of termites and assist in the digestion of
cellulose.


Giardia
intestinalis (syn. Giardia lamblia)

Cysts
are resistant forms and are responsible for transmission of giardiasis. Both
cysts and trophozoites can be found in the feces (diagnostic stages) (1) .
The cysts are hardy and can survive several months in cold water. Infection
occurs by the ingestion of cysts in contaminated water, food, or by the
fecal-oral route (hands or fomites) (2) . In the small intestine,
excystation releases trophozoites (each cyst produces two trophozoites) (3)
. Trophozoites multiply by longitudinal binary fission, remaining in the
lumen of the proximal small bowel where they can be free or attached to the
mucosa by a ventral sucking disk (4) . Encystation occurs as the parasites
transit toward the colon. The cyst is the stage found most commonly in
nondiarrheal feces (5) . Because the cysts are infectious when passed in the
stool or shortly afterward, person-to-person transmission is possible. While
animals are infected with Giardia, their importance as a reservoir is
unclear.
Geographic
Distribution:
Worldwide,
more prevalent in warm climates, and in children.


Phylum
Sarcodina


Paramecium
Moves
using cilia - short hairs lining cell
Ciliophora
Paramecium
Parts
Other
Ciliophora
Stentor
Vorticella
Spinostomium
Paramecium
Reproduction
Euglenoids




Dinoflagellates
- Pyrophyta

Diatoms
- Chrysophyta (golden algae)


Cells
Alive http://www.cellsalive.com/
Protist
Image Data http://megasun.bch.umontreal.ca/protists/protists.html